Assessment Tools
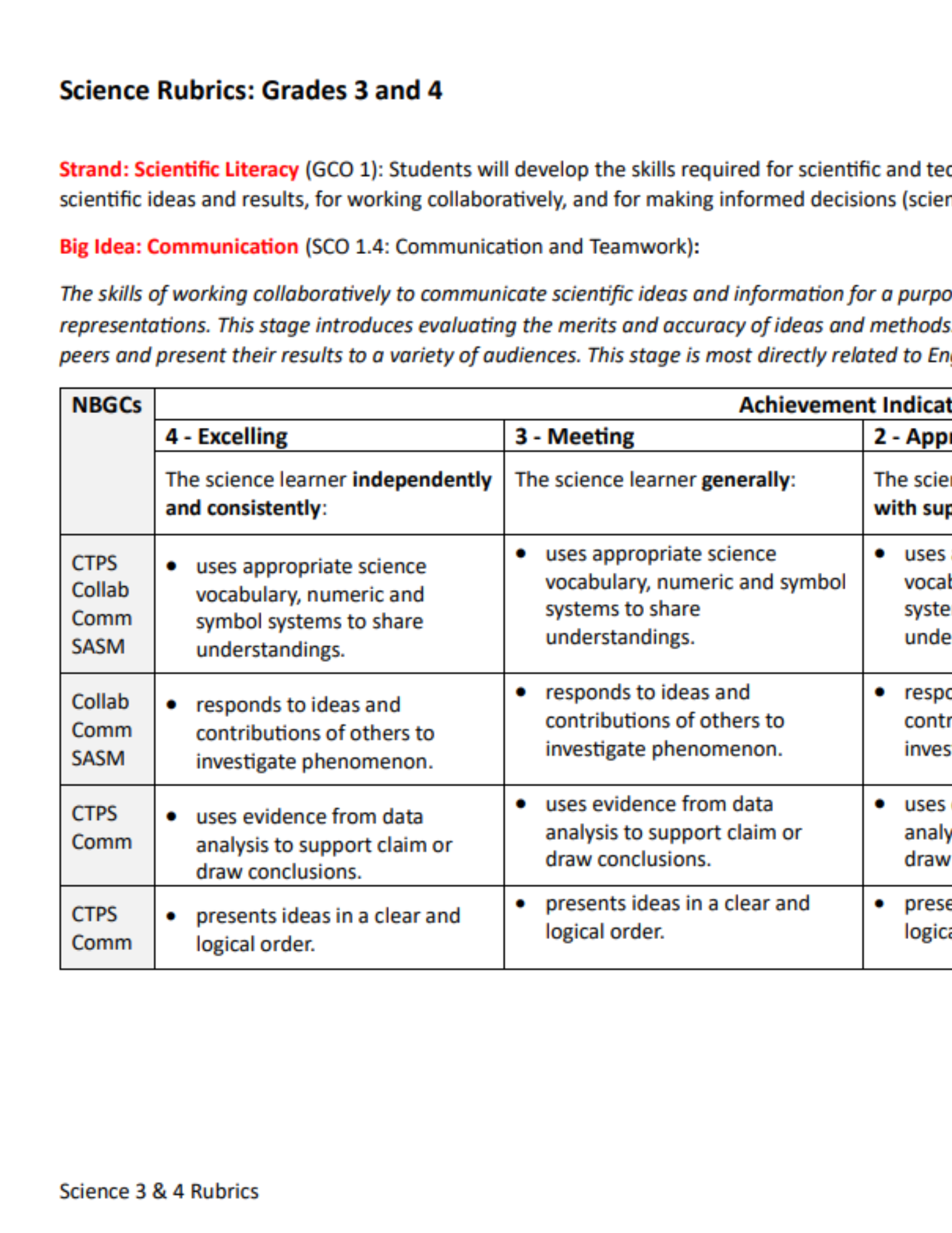
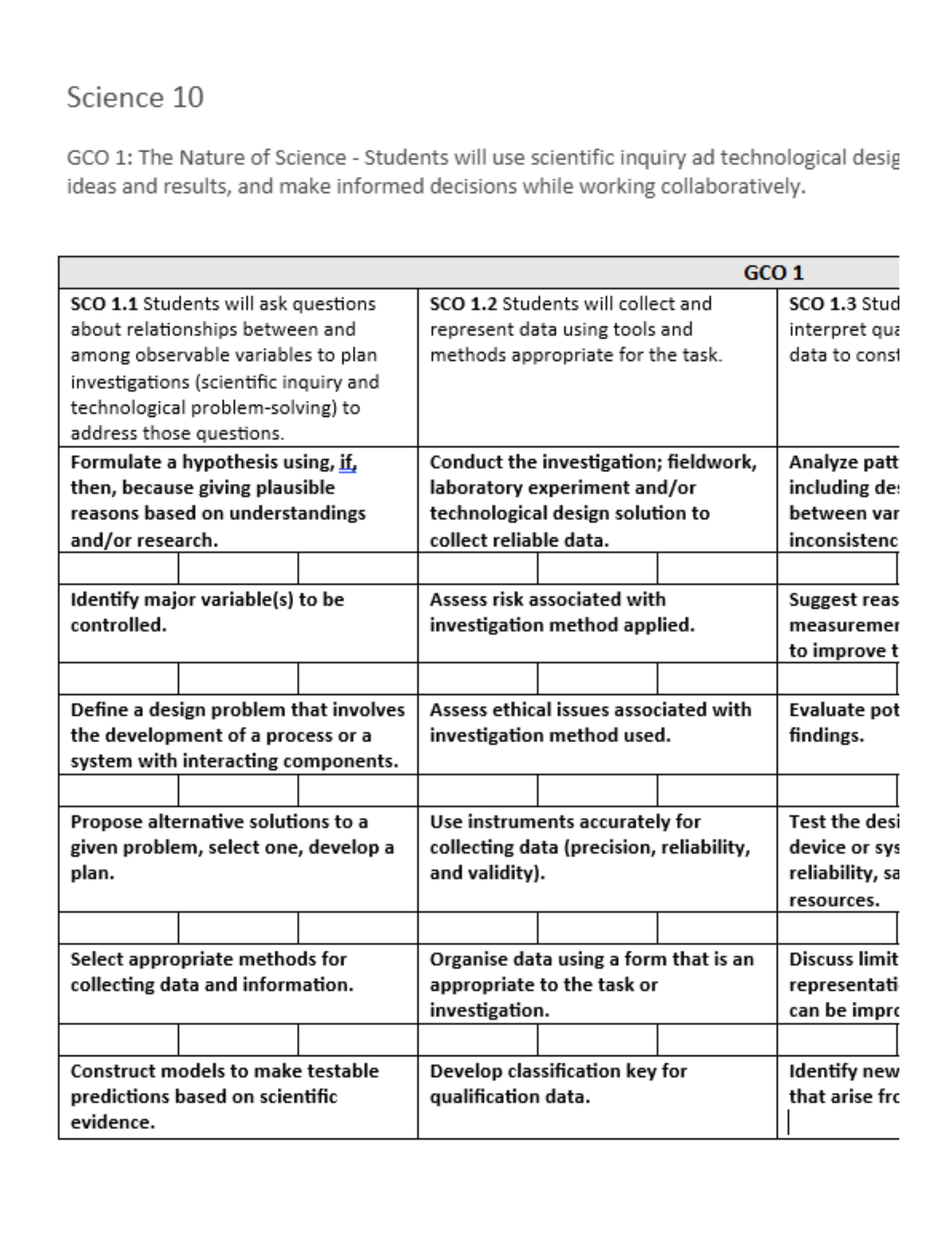
The New Brunswick model for Universal Design for Learning outlines clear principles to follow when planning for instruction and assessment in the classroom.
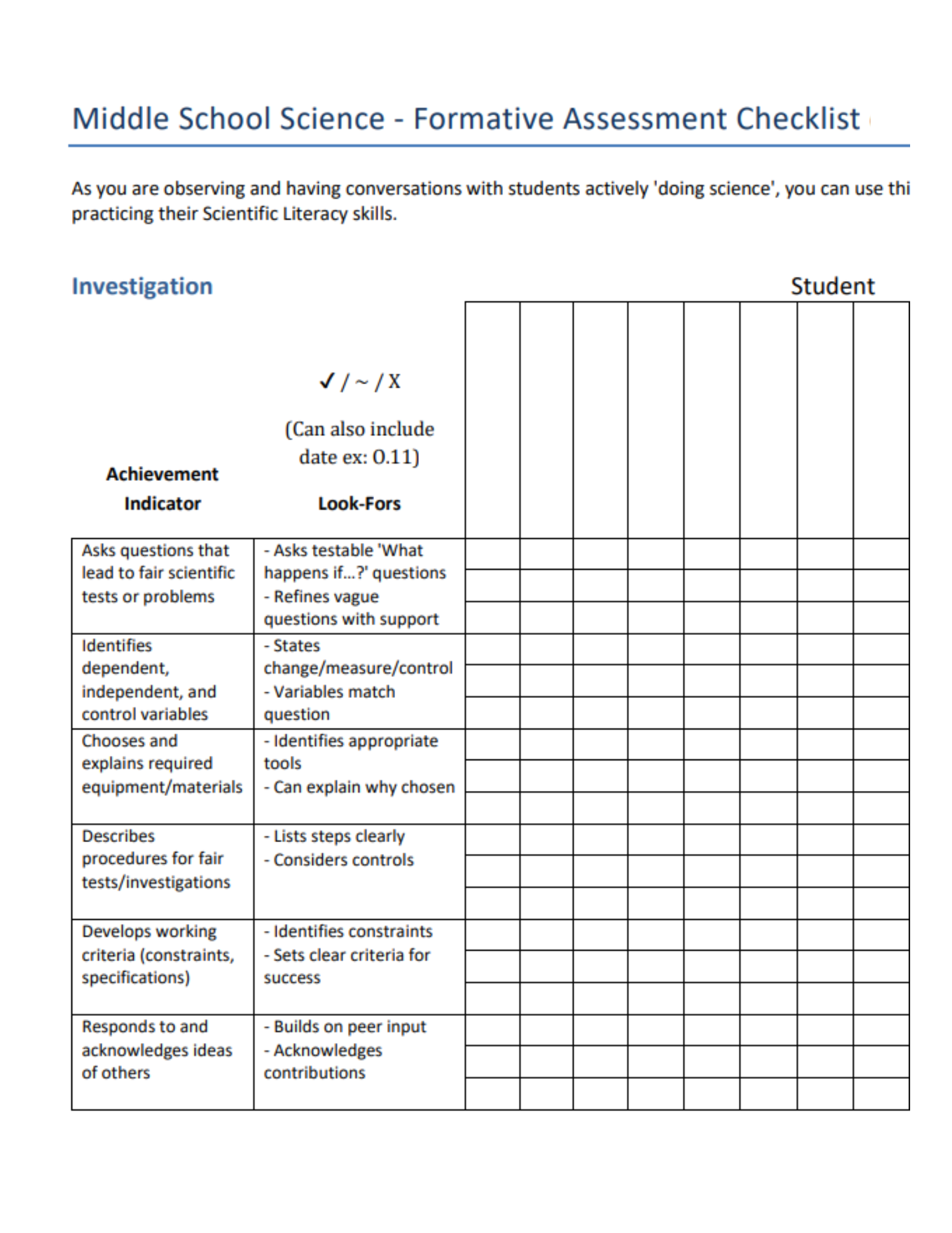
Formative assessment is a teaching and learning process that is frequent and interactive. Formative assessment provides ongoing feedback for understanding throughout the entire learning cycle: planning for learning prior to instruction; supporting learning during instruction; monitoring learning between instruction; verifying learning after instruction.
Triangulation of data involves gathering evidence from multiple sources. This increases the validity and reliability of assessment and evaluation. When learners demonstrate skills in multiple ways (observations; products; conversations), in varied contexts, there is greater certainty in achievement of learning.
Different types of evidence include:
• Observations: checklists, presentations, performance assessments, experiments being conducted
• Products: projects, quizzes, end-of-unit tests, experiments, writing samples, journals/learning logs
• Conversations: e.g., self-assessments, interviews, conferences, peer feedback
(Taken from: Assessing, Evaluating, Reporting Holistic Curriculum K-8
CURRICULUM COMPANION DOCUMENT)